What is CBD?
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is the most abundant phytocannabinoid produced by industrial hemp. CBD, unlike Δ9-THC, is non-psychoactive, meaning users of hemp will never experience the “high” associated with high-THC cannabis. Instead, CBD has been found to possess many of the other benefits of medicinal cannabis. CBD interacts with the body’s ECS to alleviate feelings of pain, anxiety, and poor sleep. Check out the bottom of this page for a full list of conditions that may be treated with CBD.
CBD comes in many forms. The most common is CBD isolate, which is 100% isolated CBD. It is a tasteless, white and powdery substance that is often added to oils or other foods and beverages to infuse them with CBD. CBD distillate is predominantly CBD but may contain trace amounts of other cannabinoids. Another form, broad spectrum, is an oil with additional cannabinoids to CBD but no THC. And full spectrum oil has the entire natural cannabinoid profile.
Each of these forms of CBD can be processed in different ways. The way an isolate or oil should be consumed depends on the way it was produced. CBD can be consumed by smoking, vaporizing, aerosol spray, oral ingestion, sublingually, topically, or suppository. Always follow the directions for use for any CBD product. Although CBD has yet to be approved by the FDA, they have allowed one CBD medicine, Epidiolex, to be used to treat two types of epilepsy disorders. Until more research is performed, we must depend on the work that has been done to understand CBD.
CBD Research
It can be difficult to find the facts on CBD. So we decided to compile the most recent and reliable research conducted on cannabidiol (CBD). We acknowledge that the current status of CBD research is still in its preliminary stages. A majority of the cited studies were performed on animals and outside the U.S. This can be attributed to restraints placed on the research of hemp by the United States Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). This restriction on CBD research has only recently been lifted with the Farm Bill of 2014, which defined industrial hemp and removed CBD from the list of Schedule 1 Substances. Now that CBD research is allowed at U.S. universities and institutions, there will be more information available soon to help us navigate the science of hemp. Please see the links below which will direct you to research papers regarding CBD and 55 different conditions.
WHO Cannabidiol (CBD) Critical Review Report
A
Acne/Skin conditions
Addiction (Alcohol, Heroin, Cigarettes)
Anxiety (Shannon et al., 2019, Blessing et al., 2015, Campos et al., 2013)
C
Cancer
Chron’s & Colitis
D
E
G
H
I
Inflammation
Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Crohn’s, Colitis
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
– More Info
– More Info
– More Info
K
L
M
Mood disorders
– Psychiatric disorders
– Regional cerebral blood flow
N
P
R
Schizophrenia
– More Info
– More Info
T
What is Full Spectrum?
Full spectrum hemp extract is regarded as the most natural form of CBD oil. The purpose of full spectrum (FS) extract is to maintain the complex compounds produced by the hemp plant. Utilizing supercritical CO₂ to create a FS oil ensures that terpenes, flavonoids, and cannabinoids are maintained from the original female flower, leading to unique flavor profiles for each hemp strain. Hemp flower is greater than the sum of its parts.
Studies have shown that cannabinoids, when isolated, are inferior to the potential benefits of the full spectrum of cannabinoids taken together. The interactions with and between each cannabinoid has been described as the “entourage effect”, or cannabinoids working in synergy.
CBD is only one of 113 phytocannabinoids synthesized by the hemp plant. While all our oils are CBD-dominant, they also contain the cannabinoids CBDA, CBGA, CBG, CBC, THCA, Δ8-THC, and Δ9-THC, which all contribute to a synergistic effect. Since our products are all full-spectrum, they do contain THC, but we can guarantee that it is always less than 0.3% Δ9-THC. At this low of a concentration, the psychoactive effects of THC are negligible.
With a CO₂ extract, we can assure a safe product free of solvents from processing, like butane or ethanol. For additional info on how FS extraction is done, visit this link from Weedmaps.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
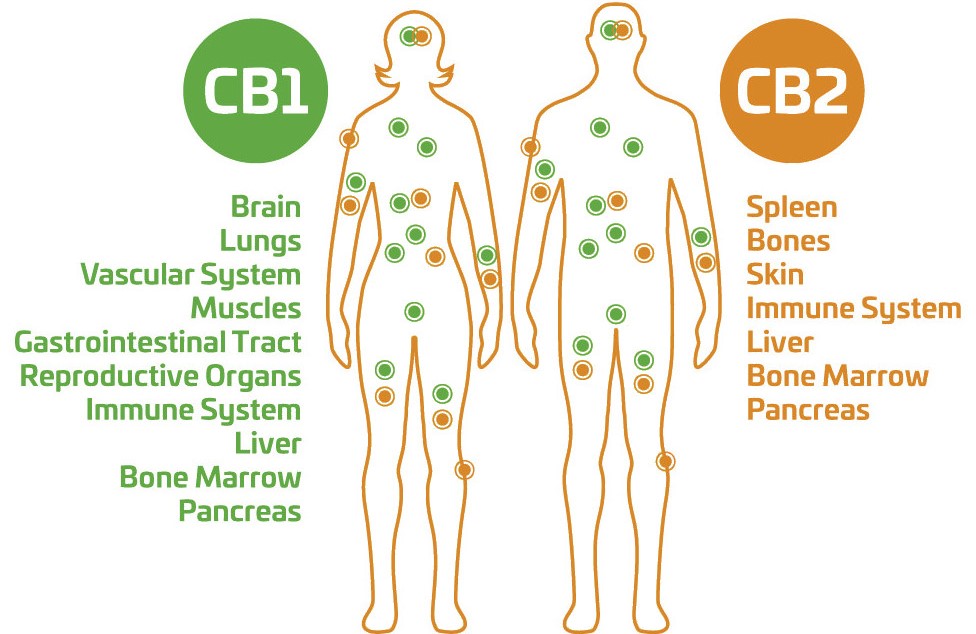
What is the endocannabinoid system (ECS)? To put it simply, the ECS is compromised of cannabinoid receptors that are found throughout the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Some preliminary research has found that the ECS may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre and postnatal development, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, memory, and mediating the effects of THC cannabis.
What are terpenes?
Terpenes are a diverse class of organic aromatic compounds commonly found in all types of plants and insects. If you have ever used an essential oil, you have experienced the effects of terpenes. Cannabis plants are unique because they contain many types of terpenes in one plant, whereas most other plants may only contain one terpene. For example, d-limonene is commonly found in lemons, limes, and oranges, but combinations of d-limonene, β-caryophyllene and α-pinene can be found in one cannabis plant.
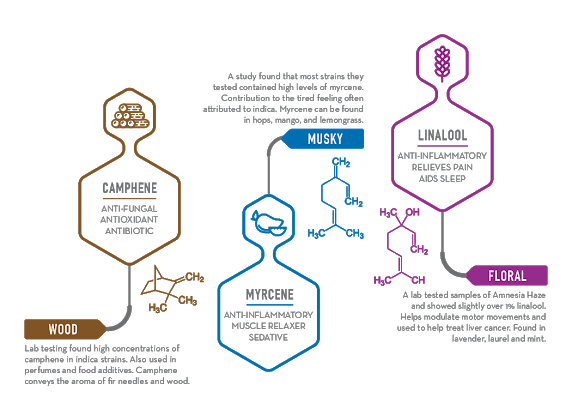
A strain like Lifter® from Oregon CBD has a combination of the terpenes β-myrcene, β-caryophyllene, cis/trans-nerolidol, and others, this is known as the cultivar’s terpene profile. These terpene profiles are specific to each strain of cannabis or hemp and are responsible for the different effects between the strains. Until recently, it was believed that the lineage of cannabis, sativa or indica, was the cause of the experienced effects, but now we know this is almost entirely due to the expressed terpene profile. More research needs to be done to fully understand how different types of strains affect the human body, but preliminary studies on individual terpenes have been promising.
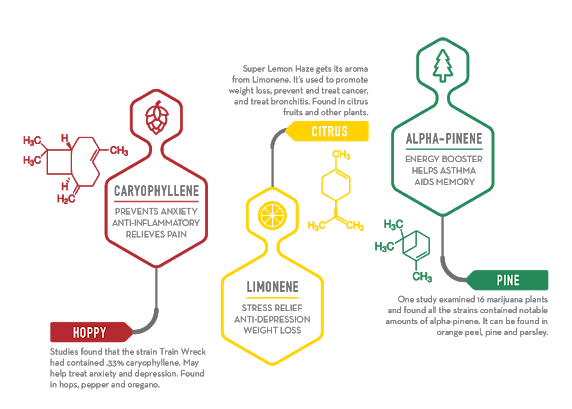
As shown in the images above, each terpene has a different effect on our bodies. The most common terpenes in cannabis are β-myrcene and β-caryophyllene. β-myrcene, also in mango and lemongrass, may have the potential to relieve pain and inflammation, protect DNA from damage, act as an antioxidant and an antimicrobial agent. β-caryophyllene, also in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon, is the only terpene known to directly interact with the ECS. With the ability to engage with cannabinoid and opioid receptors, β-caryophyllene can contribute to enhanced pain-relief. Elektra’s terpene profile is high in α-pinene, a terpene that studies have described as being anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, and anti-anxiety. Lifter® has a high concentration of cis/trans-nerolidol, which has been associated with relaxation and aid in sleep. Knowing the terpene profile of strains is essential to understand how a strain may affect your mind & body. More information on terpenes and their effects can be found at Leafly.com/terpenes.
What are flavonoids?
Flavonoids are a group of natural substances that are found in fruits, vegetables, grains, bark, roots, stems, flowers, tea, wine and hemp. They are known for their beneficial effects to our health by functioning as an anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic and anti carcinogenic properties.
Flavonoids are responsible for providing flowering hemp plants with their unique characteristics, such as deep purple color profiles. Purple strains are known to contain flavonoids such as anthoxanthins or anthocyanins. Another flavonoid found in hemp plants is cannflavin A, which one study found to have thirty times the anti-inflammatory effect as aspirin.
Unfortunately, flavonoids have been vastly understudied, which makes it difficult to make any health claims about them. What we do know is that flavonoids contribute to the “entourage effect”, which is why different hemp strains can have varying effects on our body.
Shop CBD
Find out which CBD remedy is right for you. Browse our CBD selection today!
-
-
-
1,500 mg CBD Hemp Salve
$35.00 – $60.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page